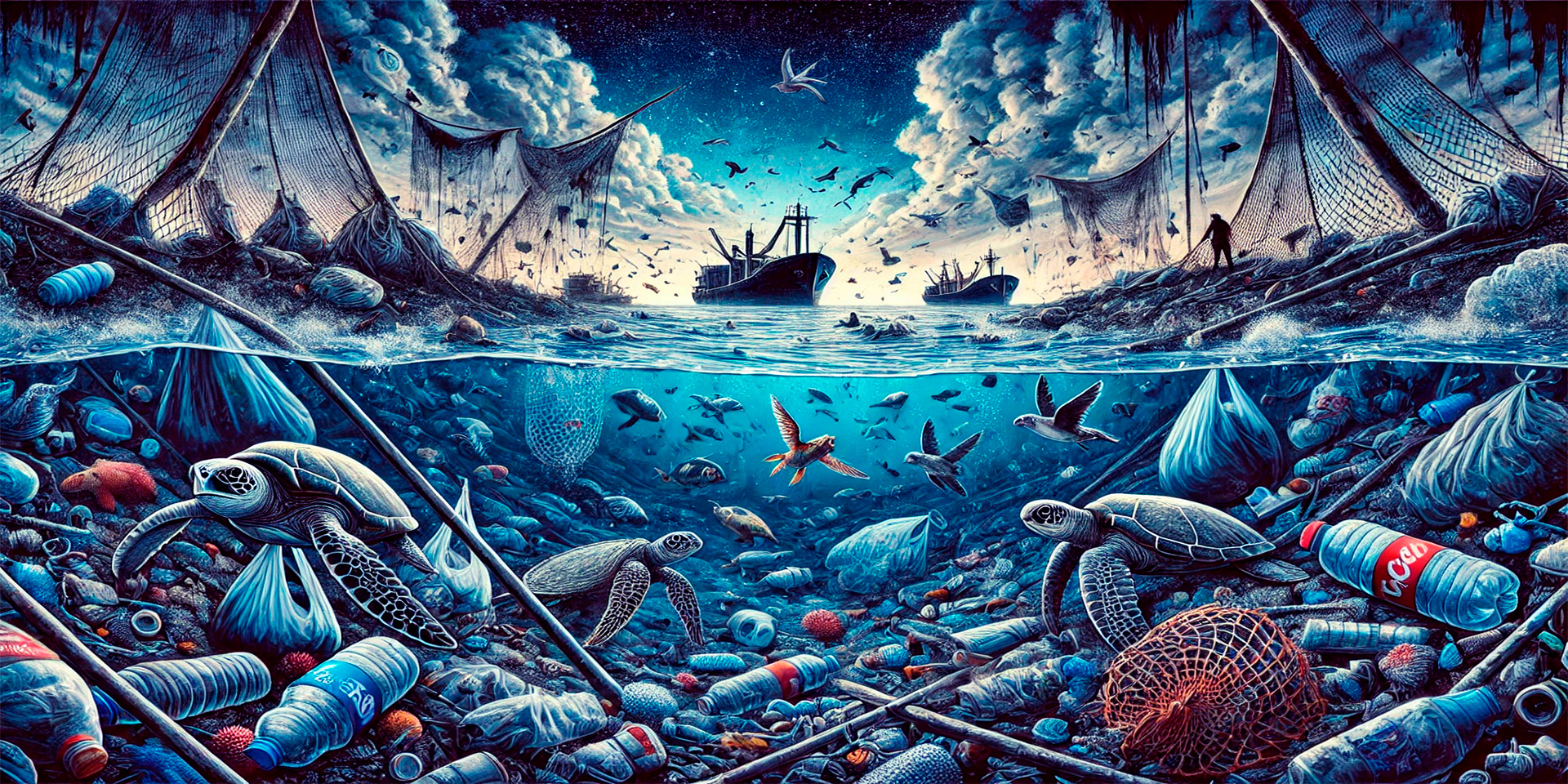
Plastic pollution is one of the most pressing environmental issues of our time, with far-reaching consequences for marine life, ecosystems, and the health of our planet. From plastic bags and bottles to microplastics and fishing gear, the sheer volume of plastic waste entering the oceans every year is staggering. This article explores the devastating effects of plastic pollution on marine life and ecosystems, how it disrupts the delicate balance of ocean environments, and the global push for sustainable solutions to address this crisis.
The Scope of the Plastic Pollution Crisis
Each year, millions of tons of plastic waste are released into the ocean, contributing to a growing environmental disaster. Plastic is durable, cheap, and widely used, which makes it an ideal material for many industries. However, its longevity and widespread usage also mean that it remains in the environment for hundreds or even thousands of years. As a result, plastic pollution has become a pervasive issue, impacting not just marine life but the entire ecosystem.
1. The Volume of Plastic in Our Oceans
According to estimates, over 8 million tons of plastic waste enter the world’s oceans every year. This staggering amount of plastic contributes to the pollution of both coastal areas and the deep ocean, affecting marine species and ecosystems across the globe. While large plastic debris such as bottles and fishing nets is visible, much of the pollution comes in the form of microplastics, tiny fragments of plastic less than 5 millimeters in size, which are even more challenging to clean up.
The scale of plastic pollution:
- Global plastic waste: Over 300 million tons of plastic are produced annually, with a large proportion of it ending up as waste in landfills or the ocean.
- Microplastics: By 2050, it is estimated that there will be more plastic in the ocean than fish, with microplastics making up a significant portion of this pollution.
- Plastic in the food chain: Studies show that plastic particles are being consumed by marine species, which can ultimately make their way into the human food chain through seafood consumption.
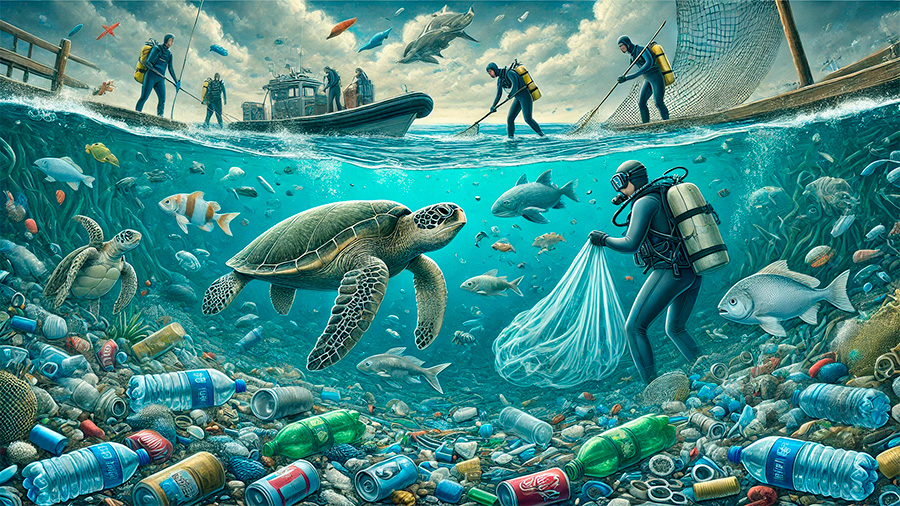

2. The Impact on Marine Life
Plastic pollution poses a serious threat to marine life. Animals, from the smallest plankton to the largest whales, are ingesting plastic debris, mistaking it for food. The ingestion of plastic can lead to choking, malnutrition, or even death. Furthermore, many marine species become entangled in plastic waste, leading to injuries, disabilities, or death.
How plastic affects marine species:
- Ingestion of plastic: Sea creatures such as turtles, fish, and seabirds often ingest plastic waste, which can cause internal injuries, blockages, and sometimes death.
- Entanglement in plastic: Large plastic debris, like fishing nets and six-pack rings, entangles marine animals, leading to drowning, loss of limbs, and impaired movement.
- Disruption of reproductive systems: Plastic pollution contains harmful chemicals, including persistent organic pollutants (POPs), which can disrupt the reproductive systems of marine life, leading to population decline.
3. Effects on Marine Ecosystems
Plastic pollution also disrupts entire marine ecosystems. Plastics, especially microplastics, are consumed by various marine organisms, entering the food chain and affecting species diversity and ecosystem health. As plastics break down, they release toxic substances into the water, further polluting the environment.
How plastic pollution disrupts ecosystems:
- Harmful toxins: As plastic breaks down in the ocean, it releases toxic chemicals such as BPA and phthalates, which harm aquatic plants and animals.
- Altered food webs: When small marine organisms consume plastic, they pass the toxins up the food chain, affecting larger predators and impacting species diversity.
- Coral reef damage: Plastic pollution can smother coral reefs, reducing the amount of sunlight that reaches the reef and harming the organisms that rely on it for survival.
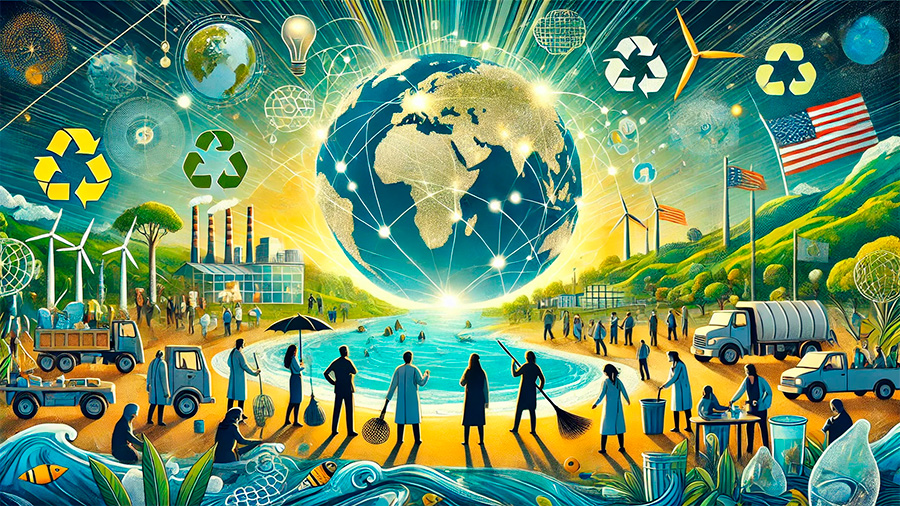

Global Efforts to Tackle Plastic Pollution
The growing awareness of plastic pollution’s impact on marine life and ecosystems has led to a global push for sustainable solutions. Governments, organizations, and individuals are coming together to reduce plastic waste, develop alternative materials, and clean up existing pollution.
1. Bans and Regulations on Single-Use Plastics
Many countries and regions have implemented bans or regulations on single-use plastics, such as plastic bags, straws, and cutlery. These measures aim to reduce plastic waste at the source and encourage the use of more sustainable alternatives. The European Union, for example, has introduced a ban on single-use plastics, including plastic cutlery and plates, in an effort to reduce marine pollution.
Examples of regulatory efforts:
- Plastic bag bans: Countries such as Kenya, India, and Rwanda have introduced strict bans on plastic bags, while many U.S. states and cities have implemented local bans or charges for plastic bags.
- Single-use plastic regulations: The EU’s ban on single-use plastics aims to significantly reduce plastic waste in marine environments by 2021.
- Extended producer responsibility (EPR): Many governments are adopting EPR laws that require manufacturers to take responsibility for the lifecycle of their products, including their disposal and recycling.
2. Innovations in Recycling and Waste Management
Innovation in recycling technologies and waste management is another critical solution to the plastic pollution crisis. Advanced recycling techniques, such as chemical recycling, allow for the breakdown of plastics into reusable materials, while waste-to-energy technologies convert plastic waste into energy.
Technological advancements in recycling:
- Chemical recycling: This process involves breaking down plastics into their chemical components, which can then be used to produce new plastics or other products, reducing the need for virgin plastic production.
- Ocean cleanup projects: Organizations like The Ocean Cleanup are working on large-scale projects to remove plastic waste from the oceans, using innovative technologies such as floating barriers to capture plastic debris.
- Waste-to-energy technologies: Some countries are using waste-to-energy technologies, converting plastic waste into usable energy, thus reducing landfill use and generating power.
3. Consumer Awareness and Behavior Change
Consumer behavior plays a pivotal role in the reduction of plastic pollution. Increased awareness about the environmental impact of plastic waste is encouraging individuals to reduce plastic consumption, choose sustainable alternatives, and participate in community clean-up efforts.
How consumers can help reduce plastic pollution:
- Reducing single-use plastics: Consumers are opting for reusable bags, containers, and utensils, thus decreasing their reliance on disposable plastics.
- Supporting sustainable brands: Many companies are now offering products with minimal plastic packaging or using biodegradable materials, and consumers can support these brands by making eco-conscious purchasing decisions.
- Participating in beach and river cleanups: Community-led initiatives are effective in removing plastic waste from shorelines and preventing it from entering the ocean.
Conclusion
Plastic pollution is one of the most significant environmental challenges facing our oceans today, with far-reaching consequences for marine life, ecosystems, and human health. The growing awareness of its devastating effects has led to a global effort to reduce plastic waste and find sustainable solutions. Through government regulations, technological innovations, and consumer behavior changes, we can begin to tackle the plastic pollution crisis and restore the health of our oceans. However, it is clear that continued collaboration and action are necessary to protect marine life and ecosystems from the ongoing threat of plastic waste.